4.6 KiB
 Que Onda
Que Onda
10 Septemeber 2024 / Document No. DYY.102.XX
Prepared By: w3th4nds
Challenge Author(s): w3th4nds
Difficulty: Very Easy
Classification: Official
Synopsis
Que Onda is a very easy difficulty challenge that features installing basic tools, interacting with netcat and basic python scripting.
Description
Que onda! Welcome to the festival of Pwn! This is a small guide to help you continue your journey, follow the instructions in README.txt
Skills Required
- None
Skills Learned
- Interaction with
ncandpwntools.
Enumeration
We are given some files, including README.txt.
$ cat README.txt
🎃 h3ll0, fr13nd5! 🎃
This challenge is designed to help you get comfortable interacting with a remote instance, while also guiding you through the installation of essential tools. If you encounter any issues or notice anything missing, feel free to reach out to me via dm (#w3th4nds).
* To install the tools, run "./tools.sh" in your terminal.
* To interact with the challenge, spawn an instance and then use the command "nc <IP> <PORT>" e.g. "nc 127.0.0.1 1337"
* To run the solver script, run "./solver.py <IP> <PORT>" or "python3 solver.py <IP> <PORT>" e.g. "python3 solver 127.0.0.1 1337"
* This "HTB{f4ke_fl4g_4_t35t1ng}" is not the flag, just a placeholder.
* After that, you simply send the string "flag" to get the flag.
* "glibc" folder is not needed to exploit the challenge, it's given so you can run the challenge.
* To run the challenge locally, enter in your terminal "./que_onda".
🎃 h4ppy h4ck1n6! 🎃
There are some basic instructions here on how to proceed with the next challenges and some helping tools to install.
$ cat tools.sh
#!/bin/bash
clear
os=$(lsb_release -i | cut -d':' -f2 | tr -d '[:space:]')
ver=$(lsb_release -d | cut -d':' -f2 | tr -d '[:space:]')
red="\e[1;32m"
green="\e[3;32m"
blue="\e[1;94m"
reset="\e[0m"
echo -ne "[!] This script will install${green} pwntools${reset},${green} gdb${reset}-${green}gef${reset} and ${green}python3-pip${reset} in your system, do you want to proceed? (Y/n): "
read ans
echo -ne "${reset}"
if [[ "$ans" == "" || "$ans" == "y" || "$ans" == "Y" ]]; then
# Install gdb - gef - python3-pip
echo -e "\n${blue}[*] $os ver: ${green}${ver}${reset}"
echo -e "\n${blue}[*] Installing${green} pwntools${blue}${reset}..\n"
sudo apt update -y
sudo apt install gdb python3-pip -y
bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://gef.blah.cat/sh)"
# Install pwntools
if [[ "$ver" == "24.0"* && "$os" == "Ububntu" ]]; then
python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip --break-system-packages && python3 -m pip install --upgrade pwntools --break-system-packages
else
python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip && python3 -m pip install --upgrade pwntools
fi
echo -e "${green}[+] Done!${reset}"
fi
This script will install python3-pip, pwntools and gdb-gef.
First interaction
First of all, we start with a checksec:
pwndbg> checksec
Arch: amd64
RELRO: Full RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
RUNPATH: b'./glibc/'
Protections 🛡️
As we can see:
| Protection | Enabled | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Canary | ✅ | Prevents Buffer Overflows |
| NX | ✅ | Disables code execution on stack |
| PIE | ✅ | Randomizes the base address of the binary |
| RelRO | Full | Makes some binary sections read-only |
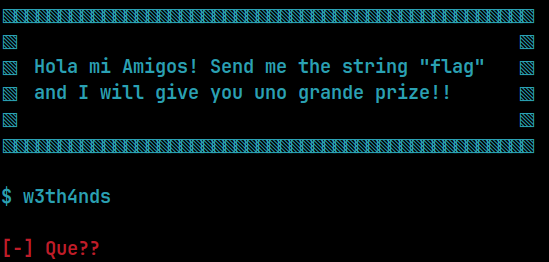
The program's interface
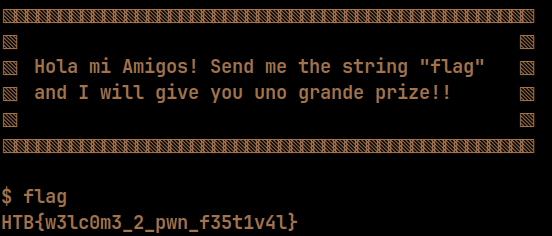
The challenge is pretty much what it says. If we send "flag", we get the flag.
Solution
#!/usr/bin/python3
from pwn import *
import warnings
import os
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
context.log_level = 'critical'
fname = './que_onda' # Specifiy the binary name
LOCAL = False # Change it to "True" to run the solver locally
os.system('clear') # Clear screen
if LOCAL:
print('Running solver locally..\n')
r = process(fname) # Starting local process
else:
IP = str(sys.argv[1]) if len(sys.argv) >= 2 else '0.0.0.0'
PORT = int(sys.argv[2]) if len(sys.argv) >= 3 else 1337
r = remote(IP, PORT) # Opens a remote connection to the specified <IP> and <PORT>
print(f'Running solver remotely at {IP} {PORT}\n')
r.sendline('flag') # Sends the string "flag" to the remote instance
print(f'Flag --> {r.recvline_contains(b"HTB")[2:].strip().decode()}\n') # Reads the flag